Copper Fox Metals: Execution Plan Released for Van Dyke; PFS Decision Next Month
- HoldCo Markets

- Sep 8, 2025
- 7 min read
DISCLAIMER: Any written content contained herein should be viewed strictly as analysis & opinion and not in any way as investment advice. Visitors to this site are encouraged to conduct their own due diligence. As a Research Spotlight product, HoldCo Markets has received financial compensation for the written content and analysis below. Please read the full disclaimer here: holdcomarkets.com/disclaimer
Copper Fox Metals (CUU) announced on September 5th that a Project Execution Plan was completed for the Van Dyke ISR Copper Project, located in Gila County, Arizona. Prepared by Stantec Consultants Services Inc., the Execution Plan outlines the complete work program and cost estimates needed to bring the project to a Pre-Feasibility (PFS) level. What makes the Execution Plan even more compelling is that it was authored by Stantec Consultants Services Inc., the very same engineering firm that worked on other notable ISR (at the time) copper projects in Arizona – notably Taseko Mines’ (TGB, TKO) Florence Project and Gunnison Copper’s (GCU) Gunnison Project (now seen as a heap leach Project). The observations, trials and conclusions found at these two earlier projects will only help to fine tune the needed roadmap for Van Dyke’s PFS. With the Execution Plan now in hand, a decision to advance Van Dyke to the PFS level will be decided by the Board before the end of October. Given the most recent close (September 5), shares of Copper Fox currently trade at a 0.13x P/NAV valuation, or at C$0.02 per booked CuEq lbs. We maintain our C$0.60 per share, 12-month price objective.

EXECUTION PLAN FINALIZED FOR THE VAN DYKE ISR DEPOSIT
The advancing and de-risking of the Van Dyke ISR copper project continues given that management now has a completed Execution Plan laying out the steps needed to advance the project to the PFS level. If approved by the Copper Fox Board (a decision is expected before the end October), the Execution Plan will serve as the road map needed to bring the project to the PFS level. Details encompassing the objectives, needed work programs and expected timelines have been outlined. Though the work requirements remain comprehensive, completion of the Execution Plan is estimated to take three years and involve a total estimated cost of $23.4M (including a 10% contingency).
ELEMENTS OF THE EXECUTION PLAN
Drilling: A two-phase drilling program was proposed. The program will focus on upgrading the mineral resource categories to meet the requirements of a PFS level study. Moreover, the drill program will allow for additional metallurgical and geotechnical sampling, and the installation of hydrogeological monitoring and water quality sampling stations. The program consists of 12,620m of reverse-circulation and diamond core drilling in 25 locations. Phase I (estimated 6 months to complete) will focus primarily on resources and consists of 11,120m in 21 holes with Phase II consisting of 1,500m in 4 holes for additional hydrogeology monitoring wells, a deeper aquifer pump test well and two geotechnical core holes if required for portal selection.
Laboratory Testwork: The Execution Plan outlined additional metallurgical, geotechnical, hydrogeological and water quality testwork to enable completion of prefeasibility studies and engineering works to support a PFS level of study. Metallurgical testing will include include sample characterization, mineralogy, locked-cycle and/or small pilot-scale leaching tests to evaluate/confirm optimum acid addition and consumption, leach cycle, and copper recovery; tracer tests to evaluate effluent conductivity over time (indicative of copper leaching progression in-situ); and pressurized rinse tests. Geotechnical testwork will include core sampling to determine rock strength and elastic properties of the Gila Conglomerate, small-scale direct shear tests, Atterberg limits testing, and USCS particle size classification of bulk samples to characterize material properties.
Updated Resource & Initial Reserve Estimates: The results of the proposed drilling program would be used to complete an updated Mineral Resource estimate (MRE) in accordance with National Instrument 43-101 standards. This would be achieved by incorporating updated geological, structural, mineral zonation and hydrogeological models, geotechnical data, and estimated copper recoveries by zone/material type. Provided that a PFS level of study is achieved, a reserve statement would be completed. The reserve estimate would quantify mineralization with reasonable expectation of economic extraction.
In-Situ Recovery, Processing & Recovery: Given that understanding the hydrogeological conditions is a significant parameter in predicting future copper production in an ISR operation, hydrogeological data would be used to determine interconnectivity between the injection and recovery wells and establish conceptual operational layouts to assist with drilling and construction diameters required for operation of injection and recovery pump equipment in operational designs. Sweep efficiencies obtained from baseline hydrogeology testing would be used to determine the operational flows required to maintain interconnectivity between injection and recovery wells within the mineralized zone.
Additional metallurgical testwork results would be used to update the Conceptual Geometallurgical Model and develop prediction algorithms for copper recovery, product quality, operating cost, throughput rates to better inform deposit variability in terms of leach kinetics, acid consumption, and deleterious elements to allow evaluation of various processing options and optimization of short- and long-term operational performance.
The eight vibrating wire piezometers (VWP) locations and three water quality monitoring locations installed during the drilling program expands the hydrogeology and groundwater coverage to establish hydraulic gradients across the site and guide water management options to better characterize the hydrogeology of the Van Dyke deposit guide water management options and support permitting efforts.
Economic Evaluation: The Plan included the use of "InEight" estimating software to an AACEI Class 4 prefeasibility level of detail. This would include a 15%/-30% (low end) to +20%/+50% (high end) level of accuracy to estimate capital and operating costs based on basic engineering with costs developed from similar ISR copper projects, benchmarked data and general arrangement drawings to develop direct, indirect and operating costs. The project's indirect costs including EPCM and owner costs would be factored based on the direct cost of the project.
Additionally, the preparation of a market study will includes the sale of copper and aggregate based on product pricing, marketability, offtake or sales agreements, long-term view of the copper market and local supply/demand for aggregate is planned for. The preparation of a financial model and sensitivity analysis following industry standards includes pre- and after-tax calculations, net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and payback period, estimated annual cash flows, operating and sustaining costs, and predicted copper sales is planned for as well.
Environmental & Permitting: The Plan contemplates development of Environmental and Water Management Plans focused on proactive waste management and waste reduction practices addressing; waste and vegetation management, water, noise, air quality and hazardous goods and outlines responsibilities, procedures, training, as well as communication, mitigation, emergency response and incident investigation and reporting, reclamation, permitting, social and community factors related to the project. The Plan outlines the estimated timeline and anticipated permitting requirements to complete the work programs required to support completion of the PFS. The project permitting strategy would be to apply for all inclusive APP and UIC permits after completion of the proposed PFS level study outlined in the Plan.
BUILDING UPON THE 2020 PRELIMINARY ECONOMIC ASSESSMENT (PEA)
In terms of economics, recall that a 2020 Van Dyke PEA used a LT copper price of $3.15 per lb and estimated a project LOM of 17 years. The economic analysis included allowances for capital, operating, sustaining, royalties, reclamation, and closure costs. The initial capital cost was estimated at $290.5M, compared to the $204.4M as estimated in a previous 2015 PEA. Given the parameters, the after-tax NPV7.5% and IRRs went from $149.5M and 27.9% in 2015 to $644.7M and 43.4% in 2020. Though from 2020, the PEA estimates are largely in line with some of the more advanced ISR projects in Arizona (mainly, Florence).

As per our estimates for Van Dyke, we acknowledge the inflationary environment which certainly since the 2020 PEA has increased materially. Cost inflation since the 2020 PEA will certainly impact everything from labor to procurement of materials to contracting. Its worth noting that using Taseko’s Florence ISR project as a guide (a Technical Report was published in 2023), we’ve seen that as construction has progressed, costs have been relatively accurate while timelines have not shifted - initial ISR production from Florence is still expected by Q4/2025. That said, we model a 16 year LOM operation at Van Dyke with a total of 1.05B lbs of copper being produced (average of 66M lbs Cu per year with peak production near 85M lbs per year). As per economics, we use a $4.50 per lb LT copper price and a $1.58 per lb C1 cash cost. Ultimately, estimating initial capex at $335M we calculate an after-tax NPV8% of $747.2M and an after-tax IRR of 34.6%.

CONCLUSION & VALUATION
We’re glad to see that work is advancing simultaneously on all projects as management has previously emphasized a systematic approach for each, in an effort to advance and de-risk, while also in an effort to allocate capital efficiently. What makes the Execution Plan even more compelling is that it was authored by Stantec Consultants Services Inc., the very same engineering firm that worked on other notable ISR (at the time) copper projects in Arizona – notably Taseko Mines’ (TGB, TKO) Florence Project and Gunnison Copper’s (GCU) Gunnison Project (now seen as a heap leach Project). The observations, trials and conclusions found at these two earlier projects will only help to fine tune the needed roadmap for Van Dyke’s PFS. With the Execution Plan now in hand, a decision to advance Van Dyke to the PFS level will be decided by the Board before the end of October. Of note is that investors are closely watching Taseko’s ramp at Florence. Given that construction and project completion was estimated to be 90% complete as of the end of June, management reiterated in August that first ISR copper production is anticipated in less than six months.
Given the most recent close (September 5), shares of Copper Fox currently trade at a 0.13x P/NAV valuation, or at C$0.02 per booked CuEq lbs. We maintain our C$0.60 per share price objective.
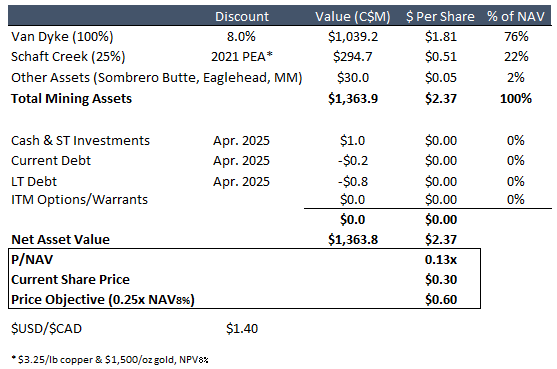

Shares of Copper Fox currently trade at attractive levels versus peers: at a 0.13x P/NAV valuation and at an EV of C$0.02 per booked CuEq lbs. Our price objective equates to upside of +100% from the most recent close. For more specific information on all the company assets, refer to our June 18, 2025 initiation of coverage piece.


