Myriad Uranium: Additional Studies = Increased Confidence in Resource Potential
- HoldCo Markets

- Oct 2, 2025
- 11 min read
DISCLAIMER: Any written content contained herein should be viewed strictly as analysis & opinion and not in any way as investment advice. Visitors to this site are encouraged to conduct their own due diligence. As a Research Spotlight product, HoldCo Markets has received financial compensation for the written content and analysis below. Please read the full disclaimer here: holdcomarkets.com/disclaimer
Myriad Uranium (M) announced on October 1 that it had obtained yet another comprehensive study estimating the uranium resource potential contained within the Copper Mountain property in Wyoming. Prepared by Bendix Field Engineering Corporation for the US Department of Energy (DOE) in 1982, the report encompasses over 600 pages of detailed data analysis and technical interpretation.
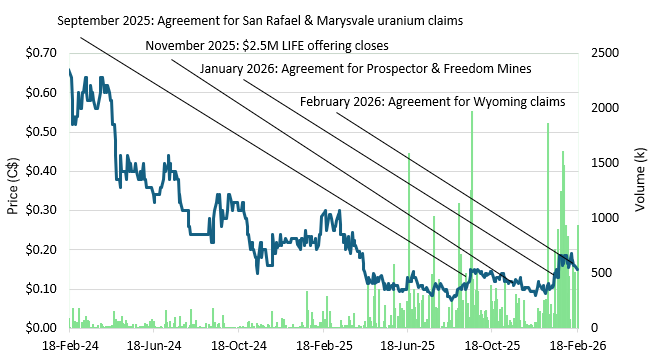
The acquisition of this latest Copper Mountain study only serves to further de-risk the Project. Given yet another comprehensive study authored by a different party, the technical data, analysis and interpretations only add to further increase our confidence level in the potential for significant uranium mineralization. Combining the data from this study with the other studies already obtained by Myriad will serve to fine-tune future drilling targets while also providing an additional roadmap for step-out and delineation drilling. Located in the uranium hotbed of Wyoming, the Copper Mountain Project is strategically located near the needed infrastructure and in close proximity to the Sweetwater uranium mill. Given the large historic resource as a starting point, assays from recent drilling indicate that Copper Mountain may yet develop to become one of the larger US uranium deposits. Now with an increased confidence level in the historic Copper Mountain resource estimate, for valuation purposes we skew our historic resource benchmark closer to the upper range, from a simple mid-point previously. Additionally, we increase our target NAV multiple, going from 0.55x to 0.60x NAV. Our new 12-month price objective of C$0.62 per share (previously C$0.54) equates to upside of +28% from the most recent close. Note that since our initiation of coverage report on August 8 2025, Myriad shares have increased by +73%.

MORE STUDIES + MORE DATA = MORE CONFIDENCE & SMARTER DRILLING TARGETS
As announced on October 1st, Myriad Uranium obtained an extensive study titled “An Exploration Systems Approach to the Copper Mountain Area Uranium Projects, Wyoming” (September 1982) authored by Bendix Field Engineering Corporation (Bendix) for the US Department of Energy (DOE). This 600 page study has proven to contain a treasure trove of valuable data including detailed data analysis and technical interpretation. Bendix had access to the entirety of Union Pacific’s vast data set, the product of C$118M (current 2025 dollars) in exploration and development spending during the 1970s. The authors also generated a considerable amount of their own data. For these reasons, though historic, the information is considered relevant and reliable and will be used by Myriad to generate its own exploration targets for project expansion. Note that previously, Myriad only had access to a summary companion document titled “Copper Mountain, Wyoming, Intermediate-Grade Uranium Resource Assessment Project Final Report” (November 1982).
CONCLUSIONS FROM THE BENDIX STUDY
With both Bendix studies now in hand, the reports cover approximately 2.5 man-years that were used in literature review, field examinations, data compilation, geologic interpretation, and final report preparation. The multi-disciplinary studies were completed during the time that Rocky Mountain Energy Corporation, a subsidiary of Union Pacific, was actively exploring in the district, and who provided property access and critical data, records, and pertinent materials on the project area. Ultimately uranium mineralization at the Copper Mountain Project was found to occur in two distinct geological settings:
Fracture-controlled uranium mineralisation hosted in Precambrian/Archaean-aged granite, syenite, isolated occurrences along the margins of diabase dikes and in association with meta-sediment inclusions in granite.
As disseminations in coarse-grained sandstones and coatings on cobbles and boulders in the Eocene/Tertiary-aged Teepee Trail Formation (Wagon Bed Group) sediments.
Three key conclusions were highlighted in the study:
A “Control Area” (17.8 km2) at Copper Mountain, centered on the Canning Deposit, was estimated to have a potential mineral endowment of approximately 245M lbs uranium down to a depth of 600ft in the intermediate grade range of 100–500 ppm eU3O8. Myriad and its partner, Rush Rare Metals Corp (RSH), hold approximately 70% of this Control Area, and an even higher percentage of the historic boreholes drilled in this area.
A larger “Assessment Area” (103 km2) was estimated to have a potential mineral endowment of approximately 655M lbs uranium, also to a depth of 600ft. Myriad and Rush hold approximately 29% of this area.
Several probable target areas for extensive intermediate-grade uranium deposits were identified by the study through structural scoring of the Assessment Area. These include locations within the Control Area that previously lacked drill-hole data, and Myriad is now aware of.
Note that detailed subsurface geologic information in the Control Area is a result of close-spaced exploration drilling. The DOE provided (with Union Pacific’s permission) data for 1,193 mineralized boreholes within the Control Area boundary. Bendix also collected its own geological, geochemical (including drilling) and geophysical data for the assessment. This high-confidence area was used for geologic modelling and structural interpretations essential to the assessment. Bendix relied on a vast amount of information for their assessment. This included detailed geological studies (general geology, tectono-depositional analysis, structure and metallogeny), surface geochemical studies (lithogeochemical, soil and stream surveys), subsurface geochemical studies (drilling, spectral radiometric probing and core geochemistry), geophysics (radiometric, magnetic and electrical methods) and emanometric (helium and radon) studies. The information was a combination of data provided by Union Pacific and data collected by Bendix.
TO UNDERSTAND COPPER MOUNTAIN IS TO UNDERSTAND THE HISTORIC STUDIES
Myriad’s key property is the Copper Mountain Uranium Project, which was recently expanded to encompass 9,320 acres. Located in central Wyoming, the project has seen extensive drilling in the late 1970s and early 1980s as both Union Pacific and California Edison planned for large scale conventional mining operations. In 1978, Rocky Mountain Energy Corporation (RMEC) estimated Copper Mountain’s resource estimate potential to be as high as 63.8M lbs when factoring in “just” 2 of the 5 identified deposits (Canning and Fuller). At a 0.01% eU3O8 grade cut-off, the resource estimate from the Canning pit alone was estimated to be 21.1M lbs U3O8. In 1980, Fluor followed-up with a study of its own (commissioned by RMEC) in what was considered to be a much more conservative estimate due to the methodology used - conditional lognormal probability distributions. Using the chosen conditional probability, Fluor applied a delayed fission neutron (DFN) adjustment which reduced the grades. Ultimately, an estimate of 14.6M lbs was calculated for Canning and parts of four other surrounding deposits (Fuller, Mint, Allard and Hesitation). Using both the RMEC and Fluor data, further studies were conducted with Gregory Liller authoring a resource estimate in 1991 and A.C.A Howe International Ltd (authored by Bojan Zabev) completing its own resource estimate in 1997. Incorporating the Canning deposit along with portions of 6 other deposits (Fuller, Mine, Allard, Hesitation, Arrowhead and Gem) these two latest reports were summarized as seeing the total resource between 15.7M lbs-30.1M lbs U3O8.
What gives Myriad a big head start with regards to developing Copper Mountain is the substantial project de-risking already achieved by way of its historic drilling program. This historic drilling program (conducted in the late 1970s) provided a vast array of technical data which lead to numerous technical reports and various resource estimates derived from different methodologies. In short, the substantial historic work conducted on the Copper Mountain Project has amounted to:
C$117M in historic exploration spent (2024 dollars).
2,000 historic boreholes drilled on the property (totaling ~900,000+ ft).
A total of 7 deposits discovered.
Numerous technical reports & resource estimates.
COPPER MOUNTAIN - HISTORY
To fully understand the mineral potential at Copper Mountain, one must first understand the history of the Project and all the work that went into estimating numerous initial resources along with additional follow-on review reports.
Mining began in 1955 at the Little Mo‐Arrowhead Mine in Eocene conglomeratic rocks of the Wagon Bed formation (also known as Teepee Trail formation) and continued to 1964 by Susquehanna Western. Western Nuclear continued production from 1968‐1970. According to the US Geological Survey (USGS), It was estimated that total uranium mining from the Copper Mountain district amounted to approximately 500,000 lbs between 1955-1970.
In terms of drilling, the most extensive drilling campaign was conducted in the 1960s and early 1970s by the Rocky Mountain Exploration Corporation (RMEC), a subsidiary of Union Carbide. According to the 2023 Technical Report, RMEC drilled approximately 2,000 boreholes in the Copper Mountain area, with each borehole averaging between 500-600 feet in depth. A large portion of the drill holes (~820) were located around the North Canning deposit in order to evaluate the deposit as a medium grade, large volume deposit for potential open pit mining. It is estimated that between 1969-1980, RMEC spent approximately $74M (in 2023 dollars) to explore and develop Copper Mountain.

With leach pads constructed and a resource estimate in hand (details below), RMEC was poised to begin mining at Copper Mountain. Unfortunately, due to the Three Mile Island nuclear incident in 1979 and the subsequent decline in uranium prices which followed, production plans were suspended.
HISTORIC RESOURCE ESTIMATES & FOLLOW-UP REVIEW REPORTS
In 1978, RMEC estimated Copper Mountain’s resource estimate potential to be as high as 63.8M lbs when factoring in “just” 2 of the 5 identified deposits (Canning and Fuller). At a 0.01% eU3O8 grade cut-off, the resource estimate from the Canning pit alone was estimated to be 21.1M lbs U3O8. In 1980, Fluor followed up with a study of its own (commissioned by RMEC) in what was considered to be a much more conservative estimate due to the methodology used - conditional lognormal probability distributions. Using the chosen conditional probability, Fluor applied a delayed fission neutron (DFN) adjustment which reduced the grades. Ultimately, an estimate of 14.6M lbs was calculated for Canning and parts of four other surrounding deposits (Fuller, Mint, Allard and Hesitation).

The Fluor estimate was reported as a “geostatistical ore reserve analysis” mostly for the Canning area however small portions from surrounding uranium deposits were also included in the analysis. Fluor’s goals as per the analysis were the following:
correction for “disequilibrium”.
construction of a three-dimensional dowel-rod model.
geostatistical structural analysis.
determination of global grade-tonnage curves.
creation of a computerized block model.
development of a bulk sampling program.
Fluor investigated various resource estimation techniques including polygonal methods, cross-sectional methods, ordinary kriging, and a method using conditional lognormal probability distributions, which was the chosen method. Use of the DFN factor to calculate grades coupled with the use of conditional lognormal probability distributions made the study somewhat controversial owing to the conservative nature of the resulting data output.
In 1991, Anaconda Resources Inc. commissioned a Summary Report on Copper Mountain, using both the RMEC and Fluor reports as a basis, however incorporating development work to date as well. The Summary Report was conducted by Gregory Liller who confirmed the Copper Mountain deposit to be not only amenable to heap leach, but also as an economically viable project (among other conclusions). In 1997, Anaconda Uranium Corporation commissioned A.C.A Howe International Ltd to prepare a second Summary Report study on the Project. Prepared by Bojan Zabev, preparation for the study included a database no included in the original reports. The Zabev report included a comparison between natural gamma probe and delayed fission neutron (DFN) derived U3O8 grades as generated by RMEC. Incorporating the Canning deposit along with portions of 6 other deposits (Fuller, Mine, Allard, Hesitation, Arrowhead and Gem) the Liller and Zabev reports were summarized as seeing the total resource between a range of 15.7M-30.1M lbs U3O8.

Though historic in nature, the vast array of geological data received from the 900,000+ ft of historic exploration conducted at Copper Mountain ultimately serves to partially de-risk the Project while also serving to provide a basis for benchmarking expectations. The various studies and methodologies applied for resource estimation also serves to study and stress test the deposit assumptions. Data from the Bendix study will further stress test and fine tune the estimates and targets going forward. A historic deposit summary ranging between 15.7M-30.1M lbs U3O8 is an excellent starting point to resume exploration activities. It is worth noting that in 1982, referencing the Bendix study, the US DOE stated that Copper Mountain’s potential may be 200M lbs in the known deposit areas. Myriad now has that full 600 page study in hand.
NEW DRILLING – MYRIAD URANIUM (2024)
When Myriad Uranium announced the conclusion of its maiden Copper Mountain drilling campaign in November, 2024, this marked the first drilling campaign on site since 1979. In total, the company drilled 34 boreholes in which initial probe results indicated over 30 intervals greater than 3.0 ft and over 1,000 ppm eU3O8. Moreover, eleven holes were able to validate the historical drilling while also delivering higher than expected grades. Just as importantly, the maiden drill program confirmed that mineralisation also occurs below the maximum depth of 500-600 ft as from the historic drilling program. As per targeted areas, Myriad’s drilling program prioritized Canning due to Union Pacific’s 1979 mine plan which identified it as the largest mineralized area and the central pit of an initial six pit mining plan. Once all assay results were received from the 34 boreholes (June 2025), it was concluded that the gamma probe results underestimated many of the grades. Of the total boreholes, the assay results indicated that the U3O8 grades were on average:
60% higher at a 1,000 ppm cut-off.
50% higher at a 500 ppm cut-off.
20% higher at a 200 ppm cut-off.
Many intervals with initially low or near-zero probe readings have been confirmed as mineralized by chemical assays. In addition to the confirmation program, one of the aims of the drilling program was to test for deeper mineralisation, below the levels that RMEC reached during its drilling program in the late 1970s (around 500-600 feet on average). Of note, Myriad’s deepest drill hole (CAN0034 – drilled to a depth of 1,556 ft) returned 832.5 ppm U3O8. This represents a 242% increase over its equivalent probe grade.

VALUATION
We continue to use the historic resource estimate as the benchmark for valuation purposes however now, incorporating the Bendix Study we have increased confidence in the potential resource endowment. That said, we increase our historic resource benchmark from 22.9M lbs (a simple mid-point from the historic lower/upper estimate) to 25.1M lbs, skewing 35/65 to the upper historic estimate. Moreover, we increase our target NAV multiple, going from 0.55x to o.60x. Given the historic nature of the resource estimate, we continue to apply our $3.25 per lb in-situ valuation. Factoring in the other assets along with corporate adjustments (a recently closed private placement), we derive a new in-situ based price objective (12 months) of C$0.62 per share (previously C$0.54 per share). This equates to potential upside of +29% from the most recent close (October 1). Note that since our initiation of coverage report on August 8 2025, Myriad shares have increased by +73%. Shares of the company currently trade at a 0.41x NAV multiple.


CONCLUSION
What gives Myriad Uranium a big head-start with regards to developing Copper Mountain is the substantial project de-risking already achieved by way of its historic drilling program. The newly acquired Bendix study only adds to further de-risk the Project while also providing additional data to further refine and fine tune the upcoming drilling program. Guided by this treasure trove of data (2,000+ historic drill holes on site), the recent and forthcoming drill program will build upon what has already been ascertained. Seeing as the recent assay results have largely surpassed grades as estimated from gamma probe testing, the potential to confirm the historic resource is apparent, but so is the potential to expand and grow the resource as well. We look forward to the additional assay results and eventual plans for an expanded drilling campaign. Pending positive drilling success and given numerous other near term catalysts, it is our opinion that the risk remains on the upside for a valuation re-rate higher. Refer to our August 8, 2025 initiation of coverage report for added details and analysis.
NEAR-TERM TIMELINE & POTENTIAL CATALYSTS
Copper Mountain assay results from an additional 8-12 drill holes
Geophysical surveys for both Copper Mountain and Red Basin.
Permit approval for an additional 20 drill holes at Copper Mountain.
Additional chemical assays of samples drilled in late 2024 to identify additional uranium which is invisible to the gamma and DFN probes.
Consolidation of the Copper Mountain Project. LOI concluding with Rush Rare Metals.
An eventual NI43-101 resource estimate for Copper Basin.
An eventual TSXV listing and/or a US listing.